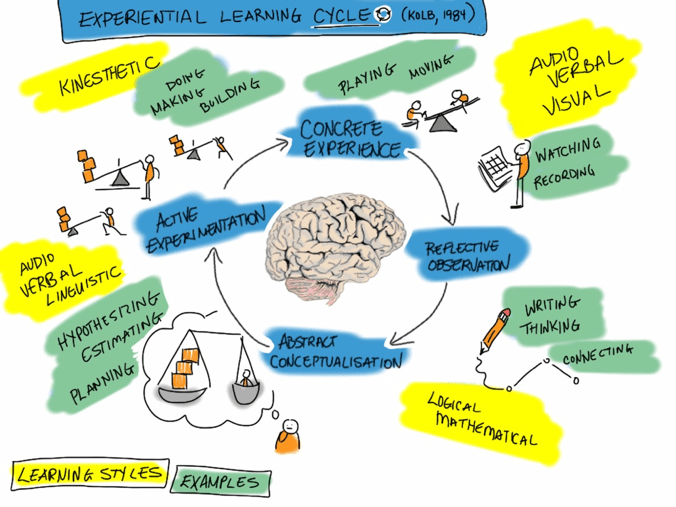
Experiential learning stems from the influences of Dewey and Piaget and in its most simplistic form can be described as “learning by doing” (University of Western Governors, 2020). The experiential learning approach asserts that humans learn best through their experiences (University of Western Governors, 2020). In practice, this learning process takes place in the classroom when teachers create opportunities and environments that provide students with real-life, practical, meaningful, and engaging learning opportunities. The benefits seen from this learning approach are endless, including giving students the opportunity to immediately apply their learned knowledge, improving student learning motivation (students are excited to learn), allowing students the opportunity for reflection, and allowing students to see real-life applications of their learning (University of Western Governors, 2020).
My group chose the topic of brain breaks for our interactive learning resource. The reason we chose this topic is that we believe in the importance of meaningful and engaging learning for all of our students. The purpose of brain breaks in the classroom is to allow students to recharge, refocus and relax after spans of listening and concentrating on a learning task. Brain breaks can be grossly simplified into three categories; physical activities, mental activities, and breathing/relaxation activities. The purpose of brain breaks is to not halt learning but to take time to absorb and reflect on what has been taught. Here we can see a connection in the objectives made to experiential learning. In experiential learning, the goal is to create meaningful learning experiences that stick out in your mind to enable you to retain and remember the information, similarly to brain breaks where the aim is to ensure learning is taking place. We can see a correlation between brain breaks and experiential learning when we look at the four stages which constitute the experiential learning cycle. In the first two stages of the cycle, the student is required to participate in a learning experience and then reflect on this experience in regard to their prior knowledge. In the second two stages, the learner focuses on transforming the given learning experience into meaningful and practical worldly practices. Amongst these four stages, we can see that there is needed time for experience, reflection, and interpretation of the learning… insert the brain break.
It is difficult to answer the question of whether I think the learning approach experiential learning belongs in our interactive learning design project about brain breaks. There is no doubt that brain breaks are integral to every learning approach/scenario to ensure meaningful and engaging learning will take place. However, to say that the two educational ideas (experiential learning and brain breaks) uniquely relate to one another is a little more abstract. An idea I can possibly envision is purposefully designing brain breaks and these transition times in a classroom to be focused on a given topic just learned… to rephrase the experiential learning could occur through an activity break based on the new learning. For example, a kindergarten class studying butterflies might undergo experiential learning by going on a field trip to Butterfly Gardens or by hatching chrysalises in the classroom. With the emphasis on the butterfly topic, a brain break activity could look like this:
- Physical break activity: Simon Says using the stages of a butterflies transformation as the questions/directions
- Mental break activity: A Kahoot butterfly life cycle challenge
- Breathing/relaxation break activity: Butterfly themed yoga
To conclude, and to decide whether or not the experiential learning approach has a place in our interactive learning design topic of brain breaks, I will say that it most definitely does, however, the idea of brain breaks also belongs and should have a place in every classroom and learning environment.
References
University of Western Governors. (2020). Teaching & Education: Experiential Learning Theory. https://www.wgu.edu/blog/experiential-learning-theory2006.html#:~:text=Experiential%20learning%20focuses%20on%20the,retain%20information%20and%20remember%20facts.
Leave a Reply